Decomposition of Data Manipulation Tasks¶
We have seen how we can complete the task of adding corresponding elements by sequentially performing the additions, one at a time, on each element of arrays A and B, placing the result in array C. Now suppose we want to put multiple processing units to work on this problem in parallel, concurrently. There are a few different ways to accomplish this. Using the example from the previous section, let’s look at one possible way that we might map the computation to processing units:
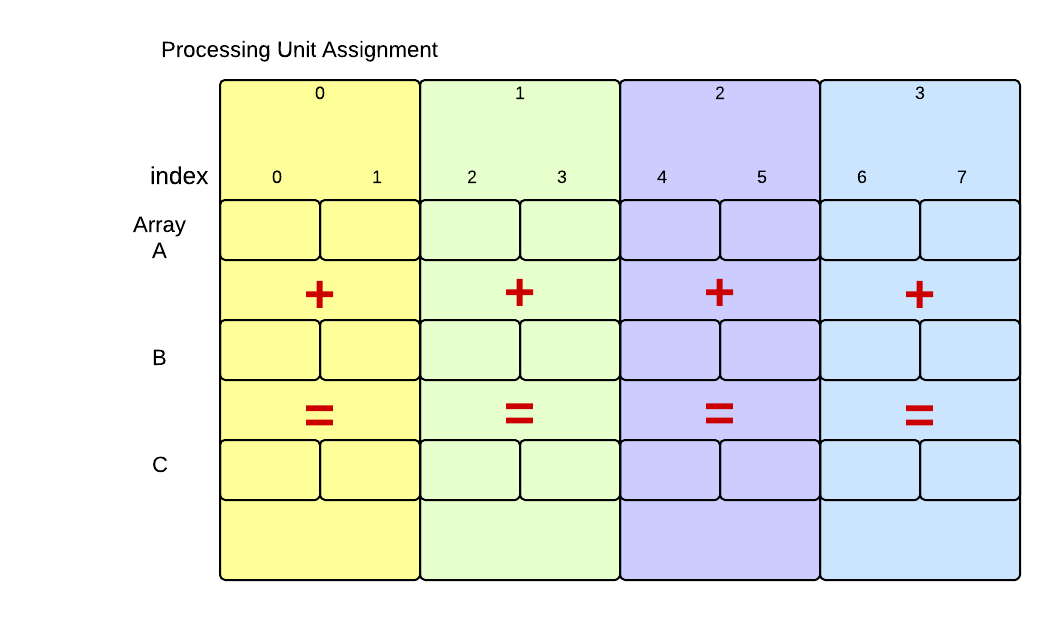
Here we see our original problem with eight elements in each array. Processing unit 0 would work on the first two elements, processing unit 1 would work on the next two, and so on. Theoretically, using four processing units executing concurrently, the work should get done in one-fourth the time it takes to run it sequentially. In practice, this never quite happens, because of the overhead to start processing units and possible contention for resources, such as the arrays themselves.
For many larger problems with more sophisticated computations, however, this type of decomposition of computational tasks on data elements is very common and can speed up your program. There is no standard terminology for this version of data decomposition; we like to refer to it as decomposing into equal-sized chunks. There are other possible types of decomposition and mapping of processing units to elements (perhaps others have been running through your mind). We limit ourselves to this particular way of decomposing, because:
- it occurs quite often,
- it is a good way to do it in many situations because elements are stored contiguously in memory, and
- you can concentrate on and learn one way of using multiple processing units.
Next we will examine example code for three combinations of parallel software and hardware:
- Message passing using the MPI library, which can be used on a cluster or a single multicore computer.
- Shared memory and threads using the OpenMP compiler directives in gcc, which can be used on a multicore computer.
- CUDA programming with the nvcc compiler, which can be used on a machine with a Graphics Procesing Unit, or GPU.
